An aggregate function in SQL performs a calculation on a set of values and returns a single value. Common aggregate functions include COUNT(), SUM(), AVG(), MAX(), and MIN().
Examples of Aggregate Functions:
Assume we have the following employees table:
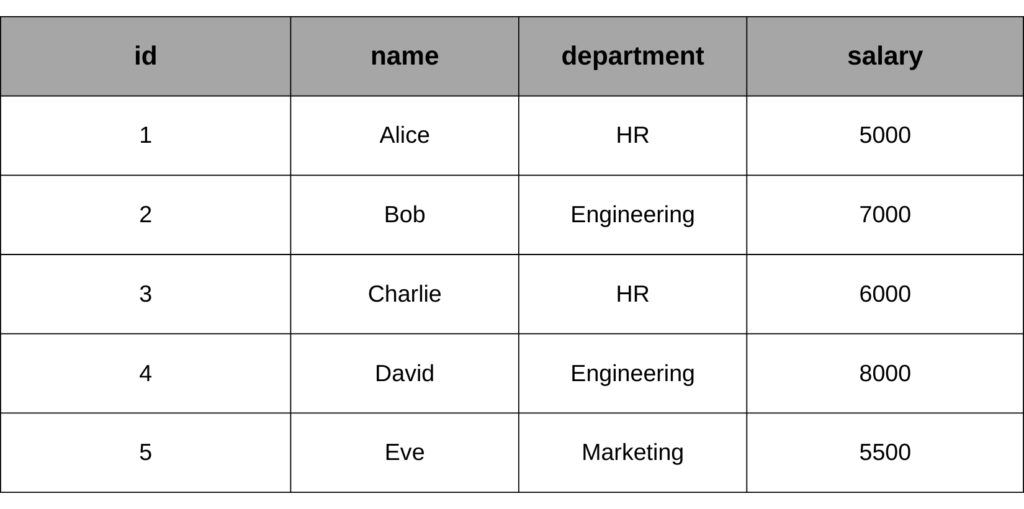
1. COUNT(): Returns the number of rows that match a specified condition.
SELECT COUNT(*) AS total_employees FROM employees;
Result:
total_employees
----------------
5
2. SUM(): Returns the sum of a numeric column.
SELECT SUM(salary) AS total_salary FROM employees;
Result:
total_salary
--------------
31500
3. AVG(): Returns the average value of a numeric column.
SELECT AVG(salary) AS average_salary FROM employees;
Result:
average_salary
----------------
6300
4. MAX(): Returns the maximum value in a set.
SELECT MAX(salary) AS highest_salary FROM employees;
Result:
highest_salary
----------------
8000
5. MIN(): Returns the minimum value in a set.
SELECT MIN(salary) AS lowest_salary FROM employees;
Result:
lowest_salary
---------------
5000
